 An automated teller machine (ATM) is a computerized telecommunications device that provides the customers of a financial institution with access to financial transactions in a public space without the need for a human clerk or bank teller.
An automated teller machine (ATM) is a computerized telecommunications device that provides the customers of a financial institution with access to financial transactions in a public space without the need for a human clerk or bank teller.Hardware
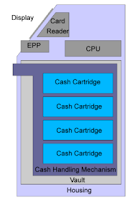
Hardware architectures using microcontrollers and/or application-specific integrated circuits to adopting a hardware architecture that is very similar to a personal computer.
Location

On most modern ATMs, the customer is identified by inserting a plastic ATM card with a magnetic stripe or a plastic smartcard with a chip that contains a unique card number and some security information, such as an expiration date or CVC (CVV). Security is provided by the customer entering a personal identification number (PIN).







